cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH
mkdir RAW_DATA
# Rename FASTQ files for 16S
for i in 16S/*_R1_001.fastq.gz ; do id=$(echo $(basename $i) | cut -d '_' -f 1) ;cp $i ${id}_R1.fastq.gz ; done
rm -f Undetermined_R1.fastq.gz
for i in 16S/*_R2_001.fastq.gz ; do id=$(echo $(basename $i) | cut -d '_' -f 1) ;cp $i ${id}_R2.fastq.gz ; done
rm -f Undetermined_R2.fastq.gz
tar zcvf 16S.tar.gz *.fastq.gz
# ITS
for i in ITS/*_R1_001.fastq.gz ; do id=$(echo $(basename $i) | cut -d '_' -f 1) ;cp $i ${id}_R1.fastq.gz ; done
rm -f Undetermined_R1.fastq.gz
for i in ITS/*_R2_001.fastq.gz ; do id=$(echo $(basename $i) | cut -d '_' -f 1) ;cp $i ${id}_R2.fastq.gz ; done
rm -f Undetermined_R2.fastq.gz
tar zcvf ITS.tar.gz *.fastq.gzLEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH
Study the bacteria and yeast diversity of Lebanese wheat sourdough, and other fermented foods by metabarcoding of 16S and ITS regions
This document is a report of the analyses performed. You will find all the code used to analyze these data. The version of the tools (maybe in code chunks) and their references are indicated, for questions of reproducibility.
Aim of the project
The aim of this project is to provide the results of the FROGS5 preprocess tool which is not yet available to the community.
Patners
- Olivier Rué - Migale/MaIAGE - INRAE
- Pamela Bechara - SPO - INRAE
- Delphine Sicard - SPO - INRAE
- Jean-Luc Legras - SPO - INRAE
- Frédéric Bigey - SPO - INRAE
Deliverables
Deliverables agreed at the preliminary meeting (Table 1).
| Definition | |
|---|---|
| 1 | HTML report |
| 2 | Archive containing data to be stored |
| 3 | BIOM, FASTA and HTML files out from FROGS5 preprocess |
| 4 | BIOM file after affiliation with METABARFOOD and UNITE sequences |
Data management
All data is managed by the migale facility for the duration of the project. Once the project is over, the Migale facility does not keep your data. We will provide you with the raw data and associated metadata that will be deposited on public repositories before the results are used. We can guide you in the submission process. We will then decide which files to keep, knowing that this report will also be provided to you and that the analyses can be replayed if needed.
Raw data
Raw data were deposited on the front server and a copy was sent to the abaca server.
Rachelle’s and Pamela’s data were then separated according to their instructions.
Here is the number of samples for each dataset:
| Dataset | Samples |
|---|---|
| Pamela 16S | 59 |
| Pamela ITS | 59 |
| Rachelle 16S | 138 |
| Rachelle ITS | 135 |
Quality control
# seqkit
cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/
mkdir -p 16S/RACHELLE 16S/PAMELA
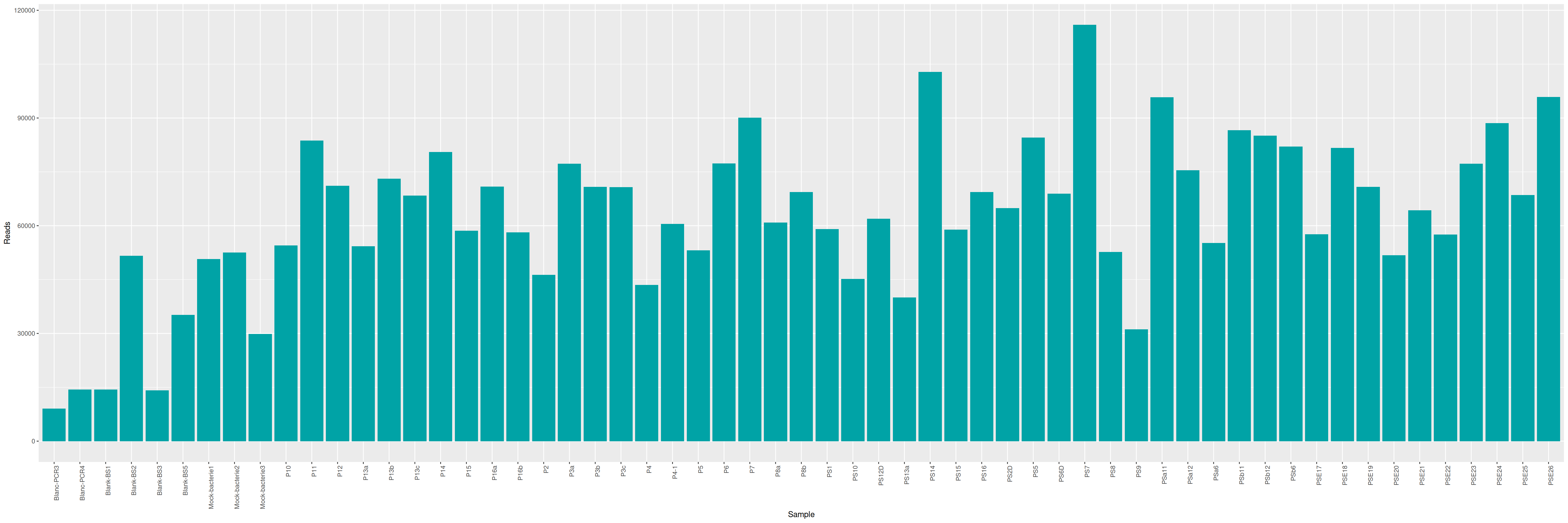
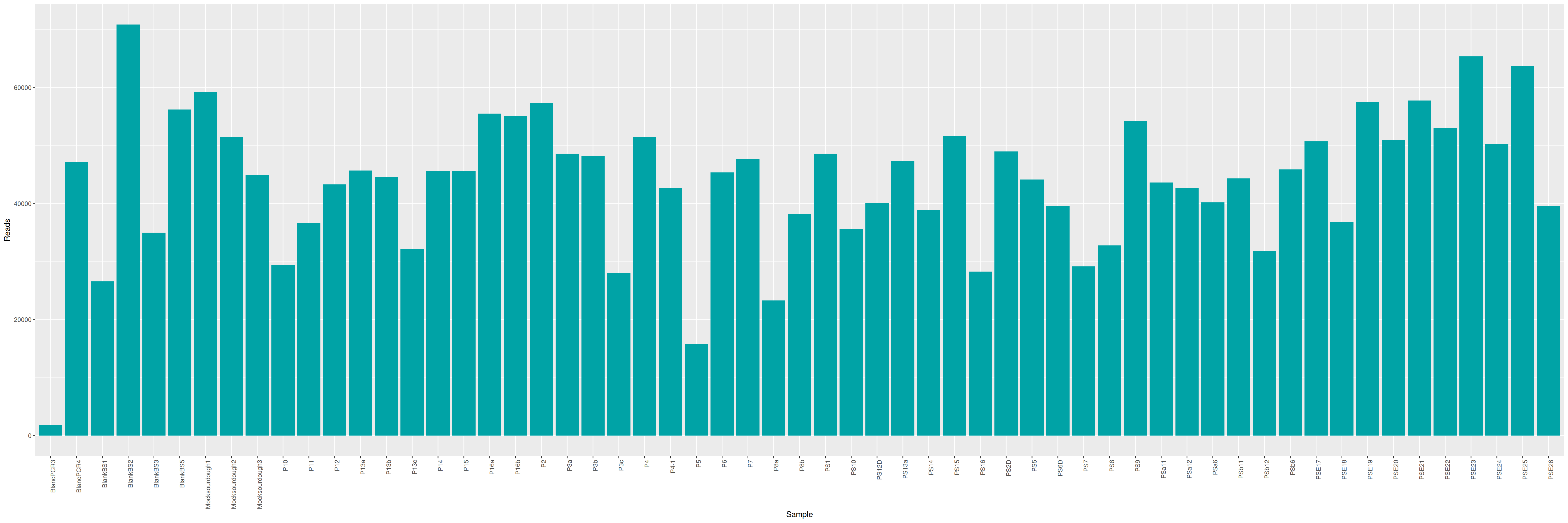
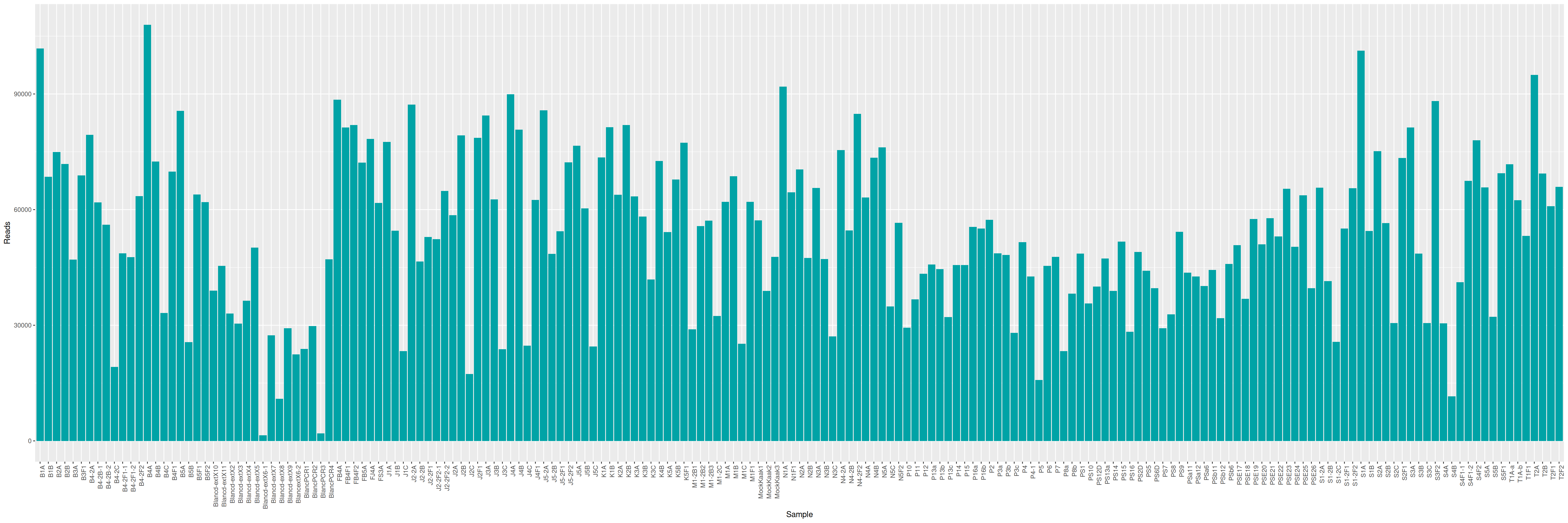
mkdir -p ITS/RACHELLE ITS/PAMELAWe can plot and display the number of reads to see if enough reads are present and if samples are homogeneous.
cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/16S/PAMELA
mkdir LOGS
qsub -cwd -V -e LOGS -o LOGS -N seqkit -pe thread 4 -R y -b y "conda activate seqkit-2.0.0 && seqkit stats /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/16S/PAMELA/*.fastq.gz -j 4 > raw_data.infos && conda deactivate"cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/ITS/PAMELA
mkdir LOGS
qsub -cwd -V -e LOGS -o LOGS -N seqkit -pe thread 4 -R y -b y "conda activate seqkit-2.0.0 && seqkit stats /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/ITS/PAMELA/*.fastq.gz -j 4 > raw_data.infos && conda deactivate"cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/16S/RACHELLE
mkdir LOGS
qsub -cwd -V -e LOGS -o LOGS -N seqkit -pe thread 4 -R y -b y "conda activate seqkit-2.0.0 && seqkit stats /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/16S/RACHELLE/*.fastq.gz -j 4 > raw_data.infos && conda deactivate"cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/ITS/RACHELLE
mkdir LOGS
qsub -cwd -V -e LOGS -o LOGS -N seqkit -pe thread 4 -R y -b y "conda activate seqkit-2.0.0 && seqkit stats /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/ITS/RACHELLE/*.fastq.gz -j 4 > raw_data.infos && conda deactivate"cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/16S/PAMELA
mkdir FASTQC
for i in /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/16S/PAMELA/*.fastq.gz ; do echo "conda activate fastqc-0.11.9 && fastqc $i -o FASTQC && conda deactivate" >> fastqc.sh ; done
qarray -cwd -V -N fastqc -o LOGS -e LOGS fastqc.sh
qsub -cwd -V -N multiqc -o LOGS -e LOGS -b y "conda activate multiqc-1.11 && multiqc FASTQC -o MULTIQC && conda deactivate"The MultiQC report shows expected metrics for Illumina Miseq sequencing data.
cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/ITS/PAMELA
mkdir FASTQC
for i in /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/ITS/PAMELA/*.fastq.gz ; do echo "conda activate fastqc-0.11.9 && fastqc $i -o FASTQC && conda deactivate" >> fastqc.sh ; done
qarray -cwd -V -N fastqc -o LOGS -e LOGS fastqc.sh
qsub -cwd -V -N multiqc -o LOGS -e LOGS -b y "conda activate multiqc-1.11 && multiqc FASTQC -o MULTIQC && conda deactivate"The MultiQC report shows expected metrics for Illumina Miseq sequencing data.
cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/16S/RACHELLE
mkdir FASTQC
for i in /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/16S/RACHELLE/*.fastq.gz ; do echo "conda activate fastqc-0.11.9 && fastqc $i -o FASTQC && conda deactivate" >> fastqc.sh ; done
qarray -cwd -V -N fastqc -o LOGS -e LOGS fastqc.sh
qsub -cwd -V -N multiqc -o LOGS -e LOGS -b y "conda activate multiqc-1.11 && multiqc FASTQC -o MULTIQC && conda deactivate"The MultiQC report shows expected metrics for Illumina Miseq sequencing data.
cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/ITS/RACHELLE
mkdir FASTQC
for i in /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/ITS/RACHELLE/*.fastq.gz ; do echo "conda activate fastqc-0.11.9 && fastqc $i -o FASTQC && conda deactivate" >> fastqc.sh ; done
qarray -cwd -V -N fastqc -o LOGS -e LOGS fastqc.sh
qsub -cwd -V -N multiqc -o LOGS -e LOGS -b y "conda activate multiqc-1.11 && multiqc FASTQC -o MULTIQC && conda deactivate"The MultiQC report shows expected metrics for Illumina Miseq sequencing data.
Bioinformatics
We used FROGS
The first tool, called preprocess allows to clean reads. From FASTQ files, reads with N were first discarded. Then, reads were denoised with dada2
cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/16S/PAMELA/
mkdir FROGS5
cd FROGS5
python $FROGS_DIR/tools/preprocess/preprocess_new.py illumina --input-archive /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/16S/PAMELA/Pamela16S.tar.gz --min-amplicon-size 300 --max-amplicon-size 590 --merge-software pear --five-prim-primer TACGGRAGGCAGCAG --three-prim-primer AGGATTAGATACCCTGGTA --R1-size 300 --R2-size 300 --nb-cpus 16 --output-dereplicated preprocess.fasta --output-fasta clusters.fasta --output-biom clusters.biom --output-count preprocess.tsv --summary preprocess.html --log-file preprocess.log --dada2cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/ITS/PAMELA/
mkdir FROGS5
cd FROGS5
python $FROGS_DIR/tools/preprocess/preprocess_new.py illumina --input-archive /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/ITS/PAMELA/PamelaITS.tar.gz --min-amplicon-size 50 --max-amplicon-size 1000 --merge-software pear --five-prim-primer CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA --three-prim-primer GCATCGATGAAGAACGCAGC --R1-size 300 --R2-size 300 --nb-cpus 16 --output-dereplicated preprocess.fasta --output-fasta clusters.fasta --output-biom clusters.biom --output-count preprocess.tsv --summary preprocess.html --log-file preprocess.log --dada2 --keep-unmergedThe affiliation with a databank constituted of UNITE v.9.0 and METABARFOOD sequences was performed from the ITSx BIOM and FASTA files. The databank build is described here.
conda activate frogs-4.1.0
cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/ITS/PAMELA/FROGS5
taxonomic_affiliation.py --input-biom itsx.biom --input-fasta itsx.fasta --nb-cpus 16 --reference ../../UNITE_9.0_20221016_plus_METABARFOOD.fasta --log-file affiliation.log --output-biom affiliation.biom --summary affiliation.html
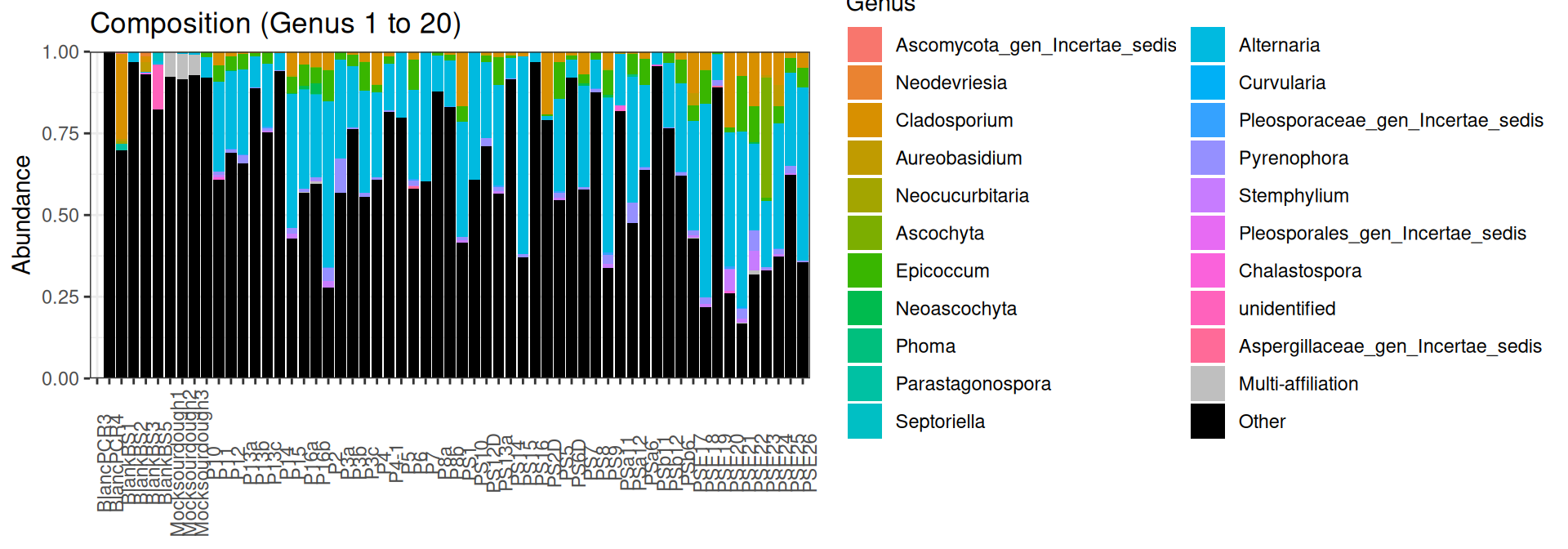
conda deactivateJust to check the taxonomies:
biomfile <- "data/pamela_ITS_metabarfood.biom"
frogs <- import_frogs(biomfile, taxMethod = "blast")
data <- data.frame("Name" = rep(1:length(sample_names(frogs))))
rownames(data) <- sample_names(frogs)
sample_data(frogs) <- data
plot_composition(frogs, taxaRank1 = NULL, taxaSet1 = NULL, taxaRank2 = "Genus", numberOfTaxa = 20)cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/16S/RACHELLE/
mkdir FROGS5
cd FROGS5
python $FROGS_DIR/tools/preprocess/preprocess_new.py illumina --input-archive /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/16S/RACHELLE/Rachelle16S.tar.gz --min-amplicon-size 300 --max-amplicon-size 590 --merge-software pear --five-prim-primer TACGGRAGGCAGCAG --three-prim-primer AGGATTAGATACCCTGGTA --R1-size 300 --R2-size 300 --nb-cpus 16 --output-dereplicated preprocess.fasta --output-fasta clusters.fasta --output-biom clusters.biom --output-count preprocess.tsv --summary preprocess.html --log-file preprocess.log --dada2cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/ITS/RACHELLE/
mkdir FROGS5
cd FROGS5
python $FROGS_DIR/tools/preprocess/preprocess_new.py illumina --input-archive /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/RAW_DATA/ITS/RACHELLE/RachelleITS.tar.gz --min-amplicon-size 50 --max-amplicon-size 1000 --merge-software pear --five-prim-primer CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA --three-prim-primer GCATCGATGAAGAACGCAGC --R1-size 300 --R2-size 300 --nb-cpus 16 --output-dereplicated preprocess.fasta --output-fasta clusters.fasta --output-biom clusters.biom --output-count preprocess.tsv --summary preprocess.html --log-file preprocess.log --dada2 --keep-unmergedThe affiliation with a databank constituted of UNITE v.9.0 and METABARFOOD sequences was performed from the ITSx BIOM and FASTA files. The databank build is described here.
conda activate frogs-4.1.0
cd /home/orue/work/PROJECTS/LEBANESEWHEATSOURDOUGH/ITS/RACHELLE/FROGS5
taxonomic_affiliation.py --input-biom itsx.biom --input-fasta itsx.fasta --nb-cpus 16 --reference ../../UNITE_9.0_20221016_plus_METABARFOOD.fasta --log-file affiliation.log --output-biom affiliation.biom --summary affiliation.html
conda deactivateDeliverables agreed at the preliminary meeting (Table 2).
| Definition | Result | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | HTML report | https://documents.migale.inrae.fr/posts/analyses/lebanesewheatsourdough-10875/ |
| 2 | Archive containing data to be stored | Deposited in the Galaxy histories of Rachelle and Pamela |
| 3 | BIOM and FASTA out from FROGS5 preprocess | Deposited in the Galaxy histories of Rachelle and Pamela |
| 4 | BIOM file after affiliation with METABARFOOD and UNITE sequences | Deposited in the Galaxy histories of Rachelle and Pamela |