#library(DT)library(tidyverse)library(kableExtra)library(phyloseq)library(phyloseq.extended)library(data.table)library(InraeThemes)library(readr) #read_delimlibrary(ggplot2) # graphicslibrary(microbiome) # for boxplot_alpha functionlibrary(mia) # microbiome analysis with SummarizedExperiment and TreeSummarizedExperimentlibrary(emmeans) #post hoc testslibrary(reactable) #table formatting and stylinglibrary(reactablefmtr) #table formatting and stylinglibrary(openxlsx) #save results to excel sheetslibrary(metacoder) # differential abundancelibrary(ggtree) # visualizationlibrary(ggtreeExtra) # visualizationlibrary(ComplexHeatmap) # produce heatmap
Note
This document is a report of the analyses performed. You will find all the code used to analyze these data. The version of the tools (maybe in code chunks) and their references are indicated, for questions of reproducibility.
Aim of the project
Influence of treatment antibiotics in a murine model of infection with Clostridium difficile (ICD). Injection of C. difficile were performed at J00 and J37.
Différencier les groupes ctrl et traités aux antibiotiques (VAN, MTZ, FDX, R = réinfections multiples), et comparer les cinétiques entre les groupes.
Etudier les cinétiques au sein des traitements (CTRL, VAN, MTZ, FDX, R). Est-ce qu’il y a un retour à J-6 ? Clairance de la bactérie (zéro dans les fécès, attention biofilm et sporulation peuvent encore existés)
All data is managed by the migale facility for the duration of the project. Once the project is over, the Migale facility does not keep your data. We will provide you with the raw data and associated metadata that will be deposited on public repositories before the results are used. We can guide you in the submission process. We will then decide which files to keep, knowing that this report will also be provided to you and that the analyses can be replayed if needed.
Analyses
Experiment
Fig1: Experimental protocol
Partie III : Etat d’eubiose
Question : les états d’eubiose sont-ils équivalents ?
Données d’entrée : objet 1 avec représentation uniquement des jours J-6, J28, J51
Figures à prévoir : • Comparaison des alpha diversité et beta diversité seulement ? ou renvoyer plutôt dans le texte aux figures précédentes.
• Analyse différentielle avec présentation des p-value nulle pour indiquer la proximité. Priorité de la figure : 2 ou 3
Phyloseq rarefied data with all samples
Show the code
frogs <-readRDS(file ="../html/frogs.rds")
For having the same sampling depth for all samples, we rarefy them before exploring the diversity.
Note that the rarefaction was performed on all samples from the complete study. We extracted samples of interest from the frogs_rare phyloseq object to calculate alpha diversity. Alpha diversity is calculated within sample and do not change with the previous analyses on the complete study.
Show the code
frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR <-subset_samples(frogs_rare, DAY %in%c("D-6", "D28", "D51") & GROUP !="R")
Taxonomic composition
After rarefaction, let’s have a look at the Phylum and genus levels composition with two types of plot.
Problematic taxa
taxa Kingdom Phylum Class Order
Cluster_40 Cluster_40 Bacteria Firmicutes Clostridia Clostridia vadinBB60 group
Family rank
Cluster_40 Unknown 8
Alpha-Diversity on subset eubiose excluding R treatment
#model <- aov(Observed ~ DAY*GROUP, data = div_data)#anova(model)#coef(model)# produce parwise comparison test with Tukey's post-hoc correction #TukeyHSD(model, which ="DAY:GROUP")alphadiv.lm <-lm(Observed ~ DAY*GROUP, data = div_data)anova(alphadiv.lm)
Analysis of Variance Table
Response: Observed
Df Sum Sq Mean Sq F value Pr(>F)
DAY 2 10402.2 5201.1 23.4782 2.979e-07 ***
GROUP 3 838.2 279.4 1.2612 0.3022
DAY:GROUP 6 1400.3 233.4 1.0535 0.4080
Residuals 36 7975.0 221.5
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Show the code
# interaction visualisationpar(mfrow =c(1,2))emmip(alphadiv.lm, GROUP ~ DAY, CIs =TRUE)
Show the code
emmip(alphadiv.lm, DAY ~ GROUP, CIs =TRUE)
Show the code
par(mfrow =c(1,1))#tests EMM <-emmeans(alphadiv.lm, ~ DAY*GROUP)# tests correction are performed within the variable# P value adjustment: tukey method for comparing a family of 12 estimatescomp1 <-pairs(EMM, simple ="DAY")# P value adjustment: tukey method for comparing a family of 5 estimates comp2 <-pairs(EMM, simple ="GROUP")
Show the code
# P value adjustment: tukey method for comparing a family of 60 estimatesres_emm <-contrast(EMM, method ="revpairwise", by =NULL,enhance.levels =c("DAY", "GROUP"), adjust ="tukey")
Important
Richness is not significantly different by GROUP and the interaction DAY:GROUP. Richness is significantly different by DAY. Pairwise tests between DAY and GROUP were performed with post hoc Tukey’s test to determine which were significant.
Important
At a fixed DAY, the means of the observed alpha diversity were not significantly different between GROUP.
Beta-diversity on subset eubiose excluding R treatment
The dissimilarity between samples based on taxonomic composition is calculated with one of these Beta diversities: Bray-Curtis, Unweighted and weighted Unifrac, Jaccard index. The Jaccard index uses presence/absence information only whereas UniFrac integrates information from the phylogenetic tree.
Show the code
# use all samples from the complete study frogs_raredist.jac <- phyloseq::distance(frogs_rare, method ="cc")dist.bc <- phyloseq::distance(frogs_rare, method ="bray")dist.uf <- phyloseq::distance(frogs_rare, method ="unifrac")dist.wuf <- phyloseq::distance(frogs_rare, method ="wunifrac")distance_list <-list("Jaccard"= dist.jac,"Bray-Curtis"= dist.bc,"UniFrac"= dist.uf,"wUniFrac"= dist.wuf)
# Mahendra's function# used own color's palette and shapemy_pcoa_with_arrows2 <-function(physeq = mydata_rare, variable1, variable2, shapeval, colorpal) {# select samples of interest where all samples were used to calculate the distances between samples # dist.jac is previously calculated with all samples of the study#dist.c <- phyloseq::distance(physeq, "jaccard") dist.c <- dist.jac %>%as.matrix() %>%`[`(sample_names(physeq), sample_names(physeq)) %>%as.dist() ord.c <-ordinate(physeq, "MDS", dist.c) p <-plot_ordination(physeq, ord.c)# ## Build arrow data plot_data <- p$data arrow_data <- plot_data %>%group_by(pick({{variable2}}, {{variable1}})) %>%arrange({{variable1}}) %>%mutate(xend = Axis.1, xstart =lag(xend),yend = Axis.2, ystart =lag(yend) )## Plot with arrows p +aes(shape = .data[[ variable2 ]], color = .data[[ variable1 ]]) +scale_shape_manual(values = shapeval) +scale_color_manual(name = colorpal$name,labels = colorpal$labels,values = colorpal$values) +theme_bw() +geom_segment(data = arrow_data,aes(x = xstart, y = ystart, xend = xend, yend = yend),size =0.8, linetype ="3131",arrow =arrow(length=unit(0.1,"inches")),show.legend =FALSE) +geom_point(size =3) +theme(legend.position ="bottom")}
Show the code
# MDS plot for samples of interests # from distance calculated with all samples of the complete study# used https://colorbrewer2.org/#type=qualitative&scheme=Paired&n=12Jour_pal <-list(name ="DAY",labels =c("D-6", "D28", "D51"),values =c("#6a3d9a", "#fdbf6f", "#e31a1c"))GROUP_shape <-list(values =c(1, 15, 16, 17))my_plot2(variable1 ="DAY",variable2 ="GROUP",physeq = frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR,shapeval = GROUP_shape$values,colorpal = Jour_pal )
We use the Jaccard distance and show MDS trajectories of the communities intra conditions.
Show the code
# MDS plot for samples of interests # from distance calculated with all samples of the complete study# used https://colorbrewer2.org/#type=qualitative&scheme=Paired&n=12Jour_pal <-list(name ="DAY",labels =c("D-6", "D28", "D51"),values =c("#6a3d9a", "#fdbf6f", "#e31a1c"))GROUP_shape <-list(values =c(1, 15, 16, 17))p <-my_pcoa_with_arrows2(variable1 ="DAY",variable2 ="GROUP",physeq = frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR,shapeval = GROUP_shape$values,colorpal = Jour_pal)p
Important
The Multidimensional scaling (MDS / PCoA) showed that samples were distributed according to the variable DAY on the first two axes. Samples from J28 and J51 are close to each other.
Permutation test for adonis under reduced model
Permutation: free
Number of permutations: 9999
vegan::adonis2(formula = dist.bc ~ DAY * GROUP, data = metadata, permutations = 9999)
Df SumOfSqs R2 F Pr(>F)
Model 11 3.1317 0.60295 4.9699 1e-04 ***
Residual 36 2.0623 0.39705
Total 47 5.1939 1.00000
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Important
The change in microbiota composition measured by the Bray-Curtis Beta diversity is significantly different between DAY, GROUP and also between the levels of the interaction factor DAY:GROUP at 0.05 significance level. The influence of the factors differs between ecosystems.
Differential abundance analysis
We performed differential analysis from frogs object without rarefaction between DAY (concerning eubiose: J-6, J28, J51) intra-treatment excluding re-infection R.
Show the code
# from Mahendra's functions# useful functions to perform a differential abundance analysis (daa)# filter taxa all zeros in all samples and # keep taxa with counts > 10 in at least the number of replicates - possibility to choosemy_filter_phyloseq <-function(physeq, nreplicates =2) { ii <- phyloseq::genefilter_sample(physeq, function(x) x >10, nreplicates) phyloseq::prune_taxa(ii, physeq)}# realise differential abundance results (daa) for the contrast# Note to specify a contrast as a listmy_extract_results <-function(deseq, test ="Wald", contrast) { DESeq2::results(deseq, test = test, tidy =TRUE, contrast = contrast) %>% dplyr::rename(ASV = row) %>%# dplyr::filter(padj <= 0.05) %>% dplyr::arrange(log2FoldChange)}# formatting the daa result by adding ASV informations into daa objectmy_format_results <-function(data, physeq) {tax_table(physeq)@.Data %>%as_tibble() %>%mutate(ASV =rownames(tax_table(physeq)@.Data)) %>% dplyr::right_join(., data, by ="ASV") %>%mutate(ASV =factor(ASV, levels = data$ASV))}# combine my_extract_results and my_format_results into an unique function# realise differential abundance results (daa) for the contrast# Note to specify a contrast as a listmy_daa_results <-function(deseq, test ="Wald", physeq, contrast) {# provide differential abundance results (daa) for the contrast# sort by log2FoldChange daa <- DESeq2::results(deseq, test = test, tidy =TRUE, contrast = contrast) %>% dplyr::rename(ASV = row) %>% dplyr::filter(padj <=0.05) # add ASV informations into daa object daa_new <-tax_table(physeq)@.Data %>%as_tibble() %>%mutate(ASV =rownames(tax_table(physeq)@.Data)) %>% dplyr::right_join(., daa, by ="ASV") %>%mutate(ASV =factor(ASV, levels = daa$ASV)) %>% dplyr::arrange(log2FoldChange)return(daa_new)}
phyloseq-class experiment-level object
otu_table() OTU Table: [ 49 taxa and 48 samples ]
sample_data() Sample Data: [ 48 samples by 7 sample variables ]
tax_table() Taxonomy Table: [ 49 taxa by 7 taxonomic ranks ]
phy_tree() Phylogenetic Tree: [ 49 tips and 48 internal nodes ]
Show the code
# do not rarefy# at defined level taxrank# filtering low abundance: less 10 in at least nreplicates# subset eubiose samplescds <- phyloseq::phyloseq_to_deseq2(frogs_eubiose,~0+ GROUPJ)rowData(cds) <-tax_table(frogs_eubiose)# cds is a summarized experiment object SE# experimental design# colData(cds)# abundances# assays(cds)$counts# fit Negative Binomial GLM modeldds <- DESeq2::DESeq(cds, sfType ="poscounts", fitType='local')dds_coeff <- DESeq2::resultsNames(dds)# define interesting contrasts# at fixed treatment between DAY in J-6, J28, J51contrast_eubiose <-list("VAN_D51vsD28"=c("GROUPJVAN_D51", "GROUPJVAN_D28"),# "VAN_D51vsD-6" = c("GROUPJVAN_D51", "GROUPJVAN_D.6"),"VAN_D28vsD-6"=c("GROUPJVAN_D28", "GROUPJVAN_D.6"),"MTZ_D51vsD28"=c("GROUPJMTZ_D51", "GROUPJMTZ_D28"),# "MTZ_D51vsD-6" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D51", "GROUPJMTZ_D.6"),"MTZ_D28vsD-6"=c("GROUPJMTZ_D28", "GROUPJMTZ_D.6"),"FDX_D51vsD28"=c("GROUPJFDX_D51", "GROUPJFDX_D28"),# "FDX_D51vsD-6" = c("GROUPJFDX_D51", "GROUPJFDX_D.6"),"FDX_D28vsD-6"=c("GROUPJFDX_D28", "GROUPJFDX_D.6"),"CTRL_D51vsD28"=c("GROUPJCTRL_D51", "GROUPJCTRL_D28"),# "CTRL_D51vsD-6" = c("GROUPJCTRL_D51", "GROUPJCTRL_D.6"),"CTRL_D28vsD-6"=c("GROUPJCTRL_D28", "GROUPJCTRL_D.6") )# # at fixed DAY between treatment# contrast_eubiose <- list(# "D-6_FDXvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJFDX_D.6", "GROUPJCTRL_D.6"),# "D-6_MTZvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D.6", "GROUPJCTRL_D.6"),# "D-6_VANvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJVAN_D.6", "GROUPJCTRL_D.6"),# "D-6_FDXvsVAN" = c("GROUPJFDX_D.6", "GROUPJVAN_D.6"),# "D-6_MTZvsVAN" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D.6", "GROUPJVAN_D.6"),# "D-6_FDXvsMTZ" = c("GROUPJFDX_D.6", "GROUPJMTZ_D.6"),# "D28_FDXvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJFDX_D28", "GROUPJCTRL_D28"),# "D28_MTZvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D28", "GROUPJCTRL_D28"),# "D28_VANvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJVAN_D28", "GROUPJCTRL_D28"),# "D28_FDXvsVAN" = c("GROUPJFDX_D28", "GROUPJVAN_D28"),# "D28_MTZvsVAN" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D28", "GROUPJVAN_D28"),# "D28_FDXvsMTZ" = c("GROUPJFDX_D28", "GROUPJMTZ_D28"), # "D51_FDXvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJFDX_D51", "GROUPJCTRL_D51"),# "D51_MTZvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D51", "GROUPJCTRL_D51"),# "D51_VANvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJVAN_D51", "GROUPJCTRL_D51"),# "D51_FDXvsVAN" = c("GROUPJFDX_D51", "GROUPJVAN_D51"),# "D51_MTZvsVAN" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D51", "GROUPJVAN_D51"),# "D51_FDXvsMTZ" = c("GROUPJFDX_D51", "GROUPJMTZ_D51") # )# realize a dda for a list of contrasts# list of differential analyses results for each contrast# daa_deseq2_eubiose <- contrast_eubiose |># map(\(x) my_extract_results(dds, contrast = list(x)))# daa_deseq2_eubiose# extract result for a fixed contrast# daa_deseq2 <- my_extract_results(dds, contrast = list(contrast_eubiose[[1]]))# format dda result for a fixed contrast# daa_res <- my_format_results(data = daa_deseq2, physeq = frogs_withoutR)# combine the previous functions# realize a differential abubdance analyses (dda) for a list of contrasts# format dda: adding ASV informations and sorting by log2FoldChangedaa_deseq2_eubiose <- contrast_eubiose |>map(\(x) my_daa_results(dds, test ="Wald", physeq = frogs_eubiose, contrast =list(x))) #daa_deseq2_eubiose#example for one contrast#res <- my_daa_results(dds, test = "Wald", contrast = list(contrast_eubiose[[1]]), physeq = frogs_eubiose)
Important
The differential abundance analysis (DAA) is based on a Generalized Linear Model (GLM) to take into account the distribution of count-type data (non-normality of the data) and over-dispersion. The regression coefficients of the factors are estimated in the model and Wald test was used to identify DAA ASV’s in a defined contrast.
Using DESeq2 R package, the GLM model [1] was fitted with one factor combining the levels of GROUP treatment and DAY factors. A Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR) correction [2] was applied on pvalues.
This is the number of differential abundance ASV obtained for each tested contrast: pairwise contrast between the levels of DAY factor intra GROUP treatment.
Show the code
# number of ASV daa for each tested contrastdaa_deseq2_eubiose |>map_df(nrow) |>t() |>kbl(col.names =c("Nb of diff. abundant ASV at Genus levels")) |>kable_styling() |>scroll_box(width ="60%", height ="200px")
Nb of diff. abundant ASV at Genus levels
VAN_D51vsD28
47
VAN_D28vsD-6
47
MTZ_D51vsD28
46
MTZ_D28vsD-6
44
FDX_D51vsD28
44
FDX_D28vsD-6
44
CTRL_D51vsD28
46
CTRL_D28vsD-6
43
Heatmap
Show the code
#vector containing DAA ASV in at least one of contrastdaa_asv <- daa_deseq2_eubiose |>map_df(\(x) dplyr::select(x, ASV)) |>t() |>as.character() |>unique()
Show the code
# abundances were agglomerated by rank = Genus# calculate a variance stabilizing transformation VST# rows (= ASV) were centered and scaled vsd <- DESeq2::varianceStabilizingTransformation(dds, fitType="local", blind =FALSE)assay(vsd) <-assay(vsd)|>t() |>scale(center =TRUE, scale =TRUE) |>t()# select eubiose samples# select daa ASVeubiose_vsd <- vsd[daa_asv,]#colData(eubiose_vsd)#assay(eubiose_vsd)#assay(eubiose_vsd)["Cluster_115",]
After the differential abundance analysis, a hierarchical clustering followed by a heatmap plot [3] were performed on DA ASV in at least one of the comparisons, with ComplexHeatmap R package.
Abundances matrix was transformed using vst function from DESeq2 R package to stabilize the variance and take into account for sequencing bias. Rows (=ASV) were centered and divided by the standard deviation.
Hierarchical clustering was performed for both rows and columns in two steps: 1/ calculate the pearson distance (1 - corr) and 2/ apply a clustering method with the Ward’s distance.
Upset plots
Important
The lists of DA ASV could be compared. UpSet plots provide a visualization for exploring more than three intersecting sets. See the Shiny application: https://intervene.shinyapps.io/intervene/ Here, a large part of DA ASV were shared between list of DA ASV.
A combination matrix with 8 sets and 12 combinations.
ranges of combination set size: c(1, 38).
mode for the combination size: distinct.
sets are on rows.
Top 8 combination sets are:
VAN_D51vsD28 VAN_D28vsD-6 MTZ_D51vsD28 MTZ_D28vsD-6 FDX_D51vsD28 FDX_D28vsD-6 CTRL_D51vsD28 CTRL_D28vsD-6 code size
x x x x x x x x 11111111 38
x x x x x x x 11111101 1
x x x x x x x 11110111 1
x x x x x x x 11011111 1
x x x x x x x 01111111 1
x x x x x x 10111110 1
x x x x x 11001110 1
x x x x 11100010 1
Sets are:
set size
VAN_D51vsD28 47
VAN_D28vsD-6 47
MTZ_D51vsD28 46
MTZ_D28vsD-6 44
FDX_D51vsD28 44
FDX_D28vsD-6 44
CTRL_D51vsD28 46
CTRL_D28vsD-6 43
Show the code
UpSet(daa_deseq2_eubiose_upset)
Description
Excel file containing the results of alpha diversity tests for eubiose samples with rarefaction based on the complete study
Excel file containing the results of differential abundance analysis concerning eubiose contrasts
2. Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B (Methodological). 1995;57:289–300. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2346101.
3. Gu Z, Eils R, Schlesner M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics. 2016;32:2847–9. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btw313.
Reuse
This document will not be accessible without prior agreement of the partners
A work by Migale Bioinformatics Facility
Université Paris-Saclay, INRAE, MaIAGE, 78350, Jouy-en-Josas, France
Université Paris-Saclay, INRAE, BioinfOmics, MIGALE bioinformatics facility, 78350, Jouy-en-Josas, France
Source Code
---title: "ICD"search: falsenavbar: falsesubtitle: "Accompaniement of Anaïs Brosse in her analyses"author: - name: Olivier Rué orcid: 0000-0003-1689-0557 email: olivier.rue@inrae.fr affiliations: - name: Migale bioinformatics facility adress: Domaine de Vilvert city: Jouy-en-Josas state: France - name: Christelle Hennequet-Antier orcid: 0000-0001-5836-2803 email: christelle.hennequet-antier@inrae.fr affiliations: - name: Migale bioinformatics facility adress: Domaine de Vilvert city: Jouy-en-Josas state: Francedate: "2023-07-05"date-modified: todayimage: "images/preview.jpg"reader-mode: falsefig-cap-location: bottomtbl-cap-location: toplicense: "This document will not be accessible without prior agreement of the partners"format: html: embed-resources: false toc: true code-fold: true code-summary: "Show the code" code-tools: true toc-location: right page-layout: article code-overflow: wrap---```{r setup, include=FALSE}knitr::opts_chunk$set(eval=TRUE, echo =TRUE, cache = TRUE, message = FALSE, warning = FALSE, cache.lazy = FALSE, fig.height = 3.5, fig.width = 10)``````{r}#| label: load-packages#library(DT)library(tidyverse)library(kableExtra)library(phyloseq)library(phyloseq.extended)library(data.table)library(InraeThemes)library(readr) #read_delimlibrary(ggplot2) # graphicslibrary(microbiome) # for boxplot_alpha functionlibrary(mia) # microbiome analysis with SummarizedExperiment and TreeSummarizedExperimentlibrary(emmeans) #post hoc testslibrary(reactable) #table formatting and stylinglibrary(reactablefmtr) #table formatting and stylinglibrary(openxlsx) #save results to excel sheetslibrary(metacoder) # differential abundancelibrary(ggtree) # visualizationlibrary(ggtreeExtra) # visualizationlibrary(ComplexHeatmap) # produce heatmap```<!-- ```{r datatable global options, echo=FALSE, eval=TRUE} --><!-- options(DT.options = list(pageLength = 10, --><!-- scrollX = TRUE, --><!-- language = list(search = 'Filter:'), --><!-- dom = 'lftipB', --><!-- buttons = c('copy', 'csv', 'excel'))) --><!-- ``` -->{{< include /resources/_includes/_intro_note.qmd >}}# Aim of the projectInfluence of treatment antibiotics in a murine model of infection with *Clostridium difficile* (ICD). Injection of *C. difficile* were performed at `J00` and `J37`.- Différencier les groupes ctrl et traités aux antibiotiques (VAN, MTZ, FDX, R = réinfections multiples), et comparer les cinétiques entre les groupes.- Etudier les cinétiques au sein des traitements (CTRL, VAN, MTZ, FDX, R). Est-ce qu’il y a un retour à J-6 ? Clairance de la bactérie (zéro dans les fécès, attention biofilm et sporulation peuvent encore existés)- Eubiose : comparer J-6, J28, J51. ## Partners* Olivier Rué - Migale bioinformatics facility - BioInfomics - INRAE* Christelle Hennequet-Antier - Migale bioinformatics facility - BioInfomics - INRAE* Mahendra Mariadassou - Migale bioinformatics facility - BioInfomics - INRAE* Anaïs Brosse - MICALIS - INRAE# Data management{{< include /resources/_includes/_data_management.qmd >}}# Analyses## Experiment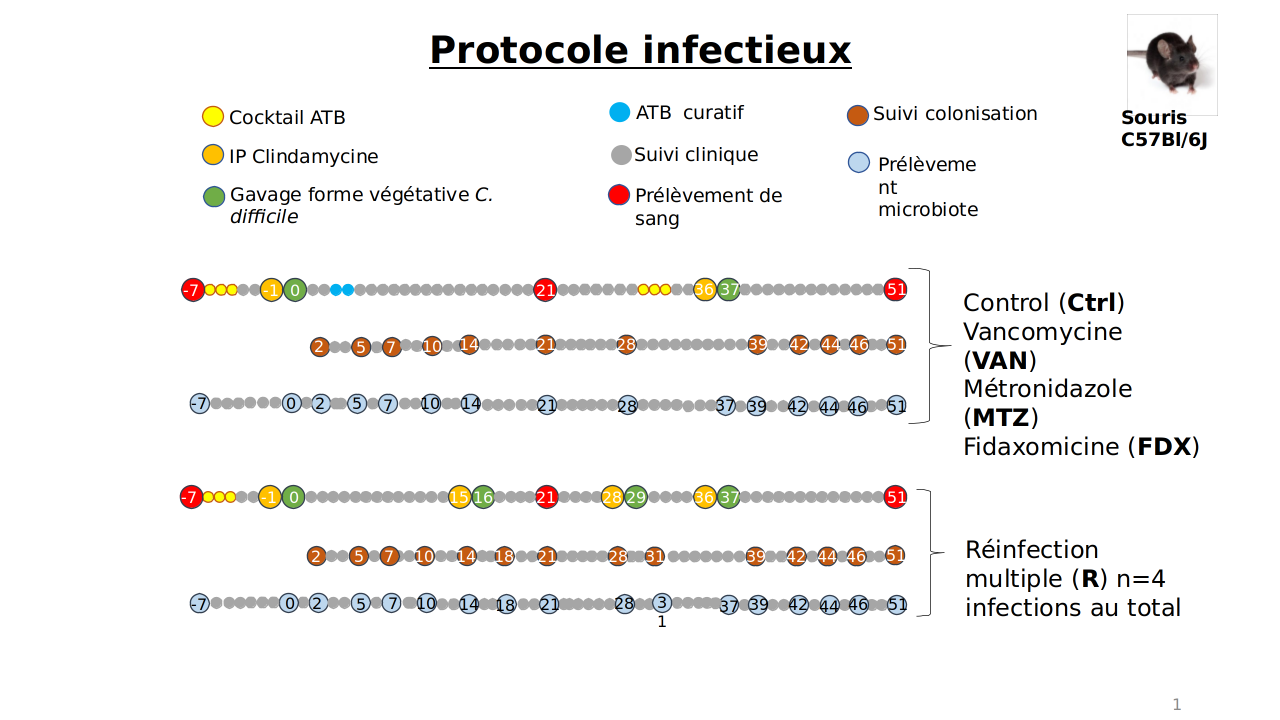{fig-align="center"}Partie III : Etat d’eubiose Question : les états d’eubiose sont-ils équivalents ? Données d’entrée : objet 1 avec représentation uniquement des jours J-6, J28, J51Figures à prévoir : • Comparaison des alpha diversité et beta diversité seulement ? ou renvoyer plutôt dans le texte aux figures précédentes. • Analyse différentielle avec présentation des p-value nulle pour indiquer la proximité. Priorité de la figure : 2 ou 3# Phyloseq rarefied data with all samples ```{r}#| label: load-datafrogs <-readRDS(file ="../html/frogs.rds")```For having the same sampling depth for all samples, we rarefy them before exploring the diversity.```{r}#| label: frogs_rarefrogs_rare <- phyloseq::rarefy_even_depth(frogs, rngseed =123, replace =TRUE)``````{r}#| echo: false#| eval: falsephyloseq::plot_bar(frogs_rare, x="REPLICAT", fill="Phylum") +facet_grid(GROUP~DAY, scales="free_x")```# study on subset eubiose excluding R treatment::: {.callout-important}Note that the rarefaction was performed on all samples from the complete study. We extracted samples of interest from the `frogs_rare` phyloseq object to calculate alpha diversity. Alpha diversity is calculated within sample and do not change with the previous analyses on the complete study.:::```{r}frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR <-subset_samples(frogs_rare, DAY %in%c("D-6", "D28", "D51") & GROUP !="R")```## Taxonomic composition After rarefaction, let's have a look at the Phylum and genus levels composition with two types of plot.We explore composition using all samples.::: {.panel-tabset}### All By GROUP```{r}#| fig-width: 20#| class: superbigimagephyloseq.extended::plot_composition(frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR, NULL, NULL, "Phylum") +facet_grid(~ GROUP + DAY, scales ="free_x", space ="free_x") +scale_fill_brewer(palette ="Paired") +theme(axis.text.x =element_text(size =6, hjust =1)) +theme(legend.position="top")```### All By grid at phylum level```{r}#| fig-height: 10phyloseq.extended::plot_composition(frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR, NULL, NULL, "Phylum", x ="SOURIS") +facet_grid(rows =vars(DAY), cols =vars(GROUP), scales ="free_x", space ="free_x") +scale_fill_brewer(palette ="Paired") +theme(axis.text.x =element_text(size =6, hjust =1)) +theme(legend.position="top")```### All By grid at family level```{r}#| fig-height: 10phyloseq.extended::plot_composition(frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR, NULL, NULL, "Family", x ="SOURIS") +facet_grid(rows =vars(DAY), cols =vars(GROUP), scales ="free_x", space ="free_x") +scale_fill_brewer(palette ="Paired") +theme(axis.text.x =element_text(size =6, hjust =1)) +theme(legend.position="top")```::: ## Alpha-Diversity on subset eubiose excluding R treatmentBoxplot of alpha-diversity facetting by `DAY`.::: {.panel-tabset}### All```{r}#| fig-height: 10# plot alpha diversity# measures = c("Observed", "Chao1", "Shannon", "Simpson", "InvSimpson")p <- phyloseq::plot_richness(physeq = frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR, x ="DAY", color="GROUP", title ="Alpha diversity graphics", measures =c("Observed", "Shannon"), nrow=5) +geom_jitter() +scale_fill_brewer(palette ="Paired") +theme(axis.text.x =element_text(size =6, angle =45, hjust =1)) +theme(legend.position="top")p```### Observed```{r}#| fig-height: 10# plot alpha diversity p.alphadiversity <- microbiome::boxplot_alpha(frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR, index ="Observed",x_var ="GROUP")p.alphadiversity +facet_grid(cols =vars(DAY), scales ="free_x", space ="free_x") +scale_fill_brewer(palette ="Paired") +theme(axis.text.x =element_text(size =6, angle =45, hjust =1)) +theme(legend.position="top")```<!-- ### Chao1 --><!-- ```{r} --><!-- #| fig-height: 10 --><!-- # plot alpha diversity --><!-- p.alphadiversity <- microbiome::boxplot_alpha(frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR, --><!-- index = "Chao1", --><!-- x_var = "GROUP") --><!-- p.alphadiversity + --><!-- facet_grid(cols = vars(DAY), scales = "free_x", space = "free_x") + --><!-- scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Paired") + --><!-- theme(axis.text.x = element_text(size = 6, angle = 45, hjust = 1)) + --><!-- theme(legend.position="top") --><!-- ``` -->### Shannon```{r}#| fig-height: 10# plot alpha diversity p.alphadiversity <- microbiome::boxplot_alpha(frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR, index ="Shannon",x_var ="GROUP")p.alphadiversity +facet_grid(cols =vars(DAY), scales ="free_x", space ="free_x") +scale_fill_brewer(palette ="Paired") +theme(axis.text.x =element_text(size =6, angle =45, hjust =1)) +theme(legend.position="top")```<!-- ### Simpson --><!-- ```{r} --><!-- #| fig-height: 10 --><!-- # plot alpha diversity --><!-- p.alphadiversity <- microbiome::boxplot_alpha(frogs_rare_withoutR, --><!-- index = "Simpson", --><!-- x_var = "GROUP") --><!-- p.alphadiversity + --><!-- facet_grid(cols = vars(DAY), scales = "free_x", space = "free_x") + --><!-- scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Paired") + --><!-- theme(axis.text.x = element_text(size = 6, angle = 45, hjust = 1)) + --><!-- theme(legend.position="top") --><!-- ``` -->:::<!-- ::: {.callout-important} --><!-- We observed that the alpha-diversity is mainly determined by `DAY` rather than `GROUP`. For each sample, the observed index measures the richness in the sample i.e. the total number of species in the community. Richness was highest in samples from `J-6` and `J51`, and also `J28` with more variability. It decreased on `J00`, and `J37` on days of infection, and increased between infection dates. The other indices do not provide any additional information, as the trajectories are consistent with infection dates. --><!-- ::: -->## Alpha-diversity - statistical testsWe calculated the alpha-diversity indices and combined them with covariates from experimental design.```{r}div_data <-cbind(estimate_richness(frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR), ## diversity indicessample_data(frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR) ## covariates )```### Model ```{r}#model <- aov(Observed ~ DAY*GROUP, data = div_data)#anova(model)#coef(model)# produce parwise comparison test with Tukey's post-hoc correction #TukeyHSD(model, which ="DAY:GROUP")alphadiv.lm <-lm(Observed ~ DAY*GROUP, data = div_data)anova(alphadiv.lm)# interaction visualisationpar(mfrow =c(1,2))emmip(alphadiv.lm, GROUP ~ DAY, CIs =TRUE)emmip(alphadiv.lm, DAY ~ GROUP, CIs =TRUE)par(mfrow =c(1,1))#tests EMM <-emmeans(alphadiv.lm, ~ DAY*GROUP)# tests correction are performed within the variable# P value adjustment: tukey method for comparing a family of 12 estimatescomp1 <-pairs(EMM, simple ="DAY")# P value adjustment: tukey method for comparing a family of 5 estimates comp2 <-pairs(EMM, simple ="GROUP")``````{r}# P value adjustment: tukey method for comparing a family of 60 estimatesres_emm <-contrast(EMM, method ="revpairwise", by =NULL,enhance.levels =c("DAY", "GROUP"), adjust ="tukey")``````{r}#| echo: false# using openxlsx package to export resultsexcelsheets <-list(All = res_emm, compbyGROUP = comp1, compbyDAY = comp2)write.xlsx(excelsheets, file =paste0("./comparisons_alpha_diversity_rareAll_eubiose_withoutR", ".xlsx"))```::: {.callout-important}Richness is not significantly different by `GROUP` and the interaction `DAY:GROUP`. Richness is significantly different by `DAY`. Pairwise tests between `DAY` and `GROUP` were performed with post hoc Tukey's test to determine which were significant.:::```{r}#| eval: true#| echo: false# https://glin.github.io/reactable/index.html# https://glin.github.io/reactable/articles/custom-filtering.html#table-search-methods# TO DO# - filter min p.value# - search contrast# color value pvalue on significance# remplir en gris lorsque p.value tukey est non signif# save# table from results of contrast# visualize estimate and p.value#comp_table <- read.xlsx(xlsxFile = "./html/comparisons_alpha_diversity.xlsx", sheet = 2)comp_table <-read.xlsx(xlsxFile ="./comparisons_alpha_diversity_rareAll_eubiose_withoutR.xlsx", sheet =2)comp_table <- comp_table %>%na.omit() %>%select(GROUP, contrast, estimate, p.value) %>%mutate(estimate =round(estimate, digits=2)) reactable(comp_table,theme =nytimes(centered =TRUE),compact =TRUE,defaultSortOrder ='asc',defaultSorted =c('GROUP', 'contrast', 'p.value'),columns =list(GROUP =colDef(name ='By Family', minWidth =70,# searchable = TRUE,# searchMethod = ),contrast =colDef(name ='comparison', minWidth =70,# searchable = TRUE,# searchMethod = ),estimate =colDef(name ='estimate',minWidth =150,align ='center',cell =data_bars(data = comp_table,text_position ='outside-end',fill_color =c('#C40233','#127852'),number_fmt = scales::label_number(accuracy =0.01) ) ),p.value =colDef(name ="Tukey's p.value",minWidth =70,align ='center',filterable =TRUE ) ))``````{r}#| eval: true#| echo: false# https://glin.github.io/reactable/index.html# https://glin.github.io/reactable/articles/custom-filtering.html#table-search-methods# TO DO# - filter min p.value# - search contrast# color value pvalue on significance# remplir en gris lorsque p.value tukey est non signif# save# table from results of contrast# visualize estimate and p.value#comp_table <- read.xlsx(xlsxFile = "./html/comparisons_alpha_diversity.xlsx", sheet = 3)comp_table <-read.xlsx(xlsxFile ="./comparisons_alpha_diversity_rareAll_eubiose_withoutR.xlsx", sheet =3)comp_table <- comp_table %>%na.omit() %>%select(DAY, contrast, estimate, p.value) %>%mutate(estimate =round(estimate, digits=2)) reactable(comp_table,theme =nytimes(centered =TRUE),compact =TRUE,defaultSortOrder ='asc',defaultSorted =c('DAY', 'contrast', 'p.value'),columns =list(DAY =colDef(name ='By Family', minWidth =70,# searchable = TRUE,# searchMethod = ),contrast =colDef(name ='comparison', minWidth =70,# searchable = TRUE,# searchMethod = ),estimate =colDef(name ='estimate',minWidth =150,align ='center',cell =data_bars(data = comp_table,text_position ='outside-end',fill_color =c('#C40233','#127852'),number_fmt = scales::label_number(accuracy =0.01) ) ),p.value =colDef(name ="Tukey's p.value",minWidth =70,align ='center',filterable =TRUE ) ))``````{r}#| eval: true#| echo: false# https://glin.github.io/reactable/index.html# https://glin.github.io/reactable/articles/custom-filtering.html#table-search-methods# TO DO# - filter min p.value# - search contrast# color value pvalue on significance# remplir en gris lorsque p.value tukey est non signif# save# # table from results of contrast# visualize estimate and p.value#comp_table <- read.xlsx(xlsxFile = "./html/comparisons_alpha_diversity.xlsx", sheet = 1)comp_table <-read.xlsx(xlsxFile ="./comparisons_alpha_diversity_rareAll_eubiose_withoutR.xlsx", sheet =1)comp_table <- comp_table %>%na.omit() %>%select(contrast, estimate, p.value) %>%mutate(estimate =round(estimate, digits=2)) # comp_table <- comp_table %>%# na.omit() %>%# select(contrast, estimate, p.value) %>%# mutate(estimate = round(estimate, digits=2)) %>%# mutate(log10p.value = -log10(p.value)) %>%# mutate(signif = case_when(# p.value < 0.05 ~ '#C40233',# p.value >= 0.05 ~ 'gray'# )# )reactable(comp_table,theme =nytimes(centered =TRUE),compact =TRUE,defaultSortOrder ='asc',defaultSorted ='p.value',columns =list(contrast =colDef(name ='comparison', minWidth =150,# searchable = TRUE,# searchMethod = ),estimate =colDef(name ='estimate',minWidth =150,align ='center',cell =data_bars(data = comp_table,text_position ='outside-end',fill_color =c('#C40233','#127852'),number_fmt = scales::label_number(accuracy =0.01) ) ),p.value =colDef(name ="Tukey's p.value",minWidth =70,align ='center',filterable =TRUE ) ))```::: {.callout-important}At a fixed `DAY`, the means of the observed alpha diversity were not significantly different between `GROUP`.:::## Beta-diversity on subset eubiose excluding R treatmentThe dissimilarity between samples based on taxonomic composition is calculated with one of these Beta diversities: Bray-Curtis, Unweighted and weighted Unifrac, Jaccard index. The Jaccard index uses presence/absence information only whereas UniFrac integrates information from the phylogenetic tree.```{r}# use all samples from the complete study frogs_raredist.jac <- phyloseq::distance(frogs_rare, method ="cc")dist.bc <- phyloseq::distance(frogs_rare, method ="bray")dist.uf <- phyloseq::distance(frogs_rare, method ="unifrac")dist.wuf <- phyloseq::distance(frogs_rare, method ="wunifrac")distance_list <-list("Jaccard"= dist.jac,"Bray-Curtis"= dist.bc,"UniFrac"= dist.uf,"wUniFrac"= dist.wuf)``````{r}#| echo: true#| eval: true# Mahendra's function# used own color's palette and shapemy_plot2 <-function(variable1, variable2, physeq = mydata_rare, shapeval, colorpal) { .plot <-function(distance) { .distance <- distance_list[[distance]] %>%as.matrix() %>%`[`(sample_names(physeq), sample_names(physeq)) %>%as.dist() p <-plot_ordination(physeq,ordinate(physeq, method ="MDS", distance = .distance),color = variable1, shape = variable2) +scale_shape_manual(values = shapeval) +scale_color_manual(name = colorpal$name,labels = colorpal$labels,values = colorpal$values ) +theme(legend.position ="none") +ggtitle(distance)# print(p) } plots <-lapply(names(distance_list), .plot) legend <- cowplot::get_legend(plots[[1]] +theme(legend.position ="bottom")) pgrid <- cowplot::plot_grid(plotlist = plots) cowplot::plot_grid(pgrid, legend, ncol =1, rel_heights =c(1, .1))}``````{r pcoa_with_arrows}#| echo: true#| eval: true# Mahendra's function# used own color's palette and shapemy_pcoa_with_arrows2 <- function(physeq = mydata_rare, variable1, variable2, shapeval, colorpal) { # select samples of interest where all samples were used to calculate the distances between samples # dist.jac is previously calculated with all samples of the study #dist.c <- phyloseq::distance(physeq, "jaccard") dist.c <- dist.jac %>% as.matrix() %>% `[`(sample_names(physeq), sample_names(physeq)) %>% as.dist() ord.c <- ordinate(physeq, "MDS", dist.c) p <- plot_ordination(physeq, ord.c) # ## Build arrow data plot_data <- p$data arrow_data <- plot_data %>% group_by(pick({{variable2}}, {{variable1}})) %>% arrange({{variable1}}) %>% mutate(xend = Axis.1, xstart = lag(xend), yend = Axis.2, ystart = lag(yend) ) ## Plot with arrows p + aes(shape = .data[[ variable2 ]], color = .data[[ variable1 ]]) + scale_shape_manual(values = shapeval) + scale_color_manual(name = colorpal$name, labels = colorpal$labels, values = colorpal$values) + theme_bw() + geom_segment(data = arrow_data, aes(x = xstart, y = ystart, xend = xend, yend = yend), size = 0.8, linetype = "3131", arrow = arrow(length=unit(0.1,"inches")), show.legend = FALSE) + geom_point(size = 3) + theme(legend.position = "bottom")}``````{r}#| fig-height: 6# MDS plot for samples of interests # from distance calculated with all samples of the complete study# used https://colorbrewer2.org/#type=qualitative&scheme=Paired&n=12Jour_pal <-list(name ="DAY",labels =c("D-6", "D28", "D51"),values =c("#6a3d9a", "#fdbf6f", "#e31a1c"))GROUP_shape <-list(values =c(1, 15, 16, 17))my_plot2(variable1 ="DAY",variable2 ="GROUP",physeq = frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR,shapeval = GROUP_shape$values,colorpal = Jour_pal )```We use the Jaccard distance and show MDS trajectories of the communities intra conditions.```{r}#| fig-height: 6# MDS plot for samples of interests # from distance calculated with all samples of the complete study# used https://colorbrewer2.org/#type=qualitative&scheme=Paired&n=12Jour_pal <-list(name ="DAY",labels =c("D-6", "D28", "D51"),values =c("#6a3d9a", "#fdbf6f", "#e31a1c"))GROUP_shape <-list(values =c(1, 15, 16, 17))p <-my_pcoa_with_arrows2(variable1 ="DAY",variable2 ="GROUP",physeq = frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR,shapeval = GROUP_shape$values,colorpal = Jour_pal)p```::: {.callout-important}The Multidimensional scaling (MDS / PCoA) showed that samples were distributed according to the variable `DAY` on the first two axes. Samples from `J28` and `J51` are close to each other. :::## Beta-diversity - Tests```{r}#| warning: falsemetadata <-sample_data(frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR) %>%as("data.frame")dist.bc <- dist.bc %>%as.matrix() %>%`[`(sample_names(frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR), sample_names(frogs_rare_eubiose_withoutR)) %>%as.dist()model <- vegan::adonis2(dist.bc ~ DAY*GROUP, data = metadata, permutations =9999)print(model)```::: {.callout-important}The change in microbiota composition measured by the `Bray-Curtis` Beta diversity is significantly different between `DAY`, `GROUP` and also between the levels of the interaction factor `DAY:GROUP` at 0.05 significance level. The influence of the factors differs between ecosystems.:::# Differential abundance analysisWe performed differential analysis from `frogs` object without rarefaction between `DAY` (concerning eubiose: J-6, J28, J51) intra-treatment excluding re-infection `R`. ```{r}#| label: my_functions_DESeq2#| echo: true#| eval: true# from Mahendra's functions# useful functions to perform a differential abundance analysis (daa)# filter taxa all zeros in all samples and # keep taxa with counts > 10 in at least the number of replicates - possibility to choosemy_filter_phyloseq <-function(physeq, nreplicates =2) { ii <- phyloseq::genefilter_sample(physeq, function(x) x >10, nreplicates) phyloseq::prune_taxa(ii, physeq)}# realise differential abundance results (daa) for the contrast# Note to specify a contrast as a listmy_extract_results <-function(deseq, test ="Wald", contrast) { DESeq2::results(deseq, test = test, tidy =TRUE, contrast = contrast) %>% dplyr::rename(ASV = row) %>%# dplyr::filter(padj <= 0.05) %>% dplyr::arrange(log2FoldChange)}# formatting the daa result by adding ASV informations into daa objectmy_format_results <-function(data, physeq) {tax_table(physeq)@.Data %>%as_tibble() %>%mutate(ASV =rownames(tax_table(physeq)@.Data)) %>% dplyr::right_join(., data, by ="ASV") %>%mutate(ASV =factor(ASV, levels = data$ASV))}# combine my_extract_results and my_format_results into an unique function# realise differential abundance results (daa) for the contrast# Note to specify a contrast as a listmy_daa_results <-function(deseq, test ="Wald", physeq, contrast) {# provide differential abundance results (daa) for the contrast# sort by log2FoldChange daa <- DESeq2::results(deseq, test = test, tidy =TRUE, contrast = contrast) %>% dplyr::rename(ASV = row) %>% dplyr::filter(padj <=0.05) # add ASV informations into daa object daa_new <-tax_table(physeq)@.Data %>%as_tibble() %>%mutate(ASV =rownames(tax_table(physeq)@.Data)) %>% dplyr::right_join(., daa, by ="ASV") %>%mutate(ASV =factor(ASV, levels = daa$ASV)) %>% dplyr::arrange(log2FoldChange)return(daa_new)}```Abundances were agglomerated at Genus taxa rank.```{r}frogs_eubiose <- frogs %>%subset_samples(DAY %in%c("D-6", "D28", "D51") & GROUP !="R") %>% phyloseq::tax_glom(., taxrank="Genus") %>%my_filter_phyloseq(., nreplicates =2)frogs_eubiose``````{r}#| label: daa_DESeq2#| echo: true#| eval: true# do not rarefy# at defined level taxrank# filtering low abundance: less 10 in at least nreplicates# subset eubiose samplescds <- phyloseq::phyloseq_to_deseq2(frogs_eubiose,~0+ GROUPJ)rowData(cds) <-tax_table(frogs_eubiose)# cds is a summarized experiment object SE# experimental design# colData(cds)# abundances# assays(cds)$counts# fit Negative Binomial GLM modeldds <- DESeq2::DESeq(cds, sfType ="poscounts", fitType='local')dds_coeff <- DESeq2::resultsNames(dds)# define interesting contrasts# at fixed treatment between DAY in J-6, J28, J51contrast_eubiose <-list("VAN_D51vsD28"=c("GROUPJVAN_D51", "GROUPJVAN_D28"),# "VAN_D51vsD-6" = c("GROUPJVAN_D51", "GROUPJVAN_D.6"),"VAN_D28vsD-6"=c("GROUPJVAN_D28", "GROUPJVAN_D.6"),"MTZ_D51vsD28"=c("GROUPJMTZ_D51", "GROUPJMTZ_D28"),# "MTZ_D51vsD-6" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D51", "GROUPJMTZ_D.6"),"MTZ_D28vsD-6"=c("GROUPJMTZ_D28", "GROUPJMTZ_D.6"),"FDX_D51vsD28"=c("GROUPJFDX_D51", "GROUPJFDX_D28"),# "FDX_D51vsD-6" = c("GROUPJFDX_D51", "GROUPJFDX_D.6"),"FDX_D28vsD-6"=c("GROUPJFDX_D28", "GROUPJFDX_D.6"),"CTRL_D51vsD28"=c("GROUPJCTRL_D51", "GROUPJCTRL_D28"),# "CTRL_D51vsD-6" = c("GROUPJCTRL_D51", "GROUPJCTRL_D.6"),"CTRL_D28vsD-6"=c("GROUPJCTRL_D28", "GROUPJCTRL_D.6") )# # at fixed DAY between treatment# contrast_eubiose <- list(# "D-6_FDXvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJFDX_D.6", "GROUPJCTRL_D.6"),# "D-6_MTZvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D.6", "GROUPJCTRL_D.6"),# "D-6_VANvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJVAN_D.6", "GROUPJCTRL_D.6"),# "D-6_FDXvsVAN" = c("GROUPJFDX_D.6", "GROUPJVAN_D.6"),# "D-6_MTZvsVAN" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D.6", "GROUPJVAN_D.6"),# "D-6_FDXvsMTZ" = c("GROUPJFDX_D.6", "GROUPJMTZ_D.6"),# "D28_FDXvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJFDX_D28", "GROUPJCTRL_D28"),# "D28_MTZvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D28", "GROUPJCTRL_D28"),# "D28_VANvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJVAN_D28", "GROUPJCTRL_D28"),# "D28_FDXvsVAN" = c("GROUPJFDX_D28", "GROUPJVAN_D28"),# "D28_MTZvsVAN" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D28", "GROUPJVAN_D28"),# "D28_FDXvsMTZ" = c("GROUPJFDX_D28", "GROUPJMTZ_D28"), # "D51_FDXvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJFDX_D51", "GROUPJCTRL_D51"),# "D51_MTZvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D51", "GROUPJCTRL_D51"),# "D51_VANvsCTRL" = c("GROUPJVAN_D51", "GROUPJCTRL_D51"),# "D51_FDXvsVAN" = c("GROUPJFDX_D51", "GROUPJVAN_D51"),# "D51_MTZvsVAN" = c("GROUPJMTZ_D51", "GROUPJVAN_D51"),# "D51_FDXvsMTZ" = c("GROUPJFDX_D51", "GROUPJMTZ_D51") # )# realize a dda for a list of contrasts# list of differential analyses results for each contrast# daa_deseq2_eubiose <- contrast_eubiose |># map(\(x) my_extract_results(dds, contrast = list(x)))# daa_deseq2_eubiose# extract result for a fixed contrast# daa_deseq2 <- my_extract_results(dds, contrast = list(contrast_eubiose[[1]]))# format dda result for a fixed contrast# daa_res <- my_format_results(data = daa_deseq2, physeq = frogs_withoutR)# combine the previous functions# realize a differential abubdance analyses (dda) for a list of contrasts# format dda: adding ASV informations and sorting by log2FoldChangedaa_deseq2_eubiose <- contrast_eubiose |>map(\(x) my_daa_results(dds, test ="Wald", physeq = frogs_eubiose, contrast =list(x))) #daa_deseq2_eubiose#example for one contrast#res <- my_daa_results(dds, test = "Wald", contrast = list(contrast_eubiose[[1]]), physeq = frogs_eubiose) ``````{r}#| echo: false# save dda for each contrast in excel file# using openxlsx package to export resultswrite.xlsx(daa_deseq2_eubiose, file =paste0("./daa_deseq2_eubiose_withoutR", ".xlsx"))```::: {.callout-important}The differential abundance analysis (DAA) is based on a Generalized Linear Model (GLM) to take into account the distribution of count-type data (non-normality of the data) and over-dispersion. The regression coefficients of the factors are estimated in the model and Wald test was used to identify DAA ASV's in a defined contrast.Using **DESeq2** {{< iconify mdi tools >}} R package, the GLM model [@Love-DESeq2] was fitted with one factor combining the levels of `GROUP` treatment and `DAY` factors. A Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR) correction [@Benjamini1995] was applied on pvalues.:::This is the number of differential abundance ASV obtained for each tested contrast: pairwise contrast between the levels of `DAY` factor intra `GROUP` treatment.```{r}# number of ASV daa for each tested contrastdaa_deseq2_eubiose |>map_df(nrow) |>t() |>kbl(col.names =c("Nb of diff. abundant ASV at Genus levels")) |>kable_styling() |>scroll_box(width ="60%", height ="200px")```# Heatmap```{r}#vector containing DAA ASV in at least one of contrastdaa_asv <- daa_deseq2_eubiose |>map_df(\(x) dplyr::select(x, ASV)) |>t() |>as.character() |>unique() ``````{r}# abundances were agglomerated by rank = Genus# calculate a variance stabilizing transformation VST# rows (= ASV) were centered and scaled vsd <- DESeq2::varianceStabilizingTransformation(dds, fitType="local", blind =FALSE)assay(vsd) <-assay(vsd)|>t() |>scale(center =TRUE, scale =TRUE) |>t()# select eubiose samples# select daa ASVeubiose_vsd <- vsd[daa_asv,]#colData(eubiose_vsd)#assay(eubiose_vsd)#assay(eubiose_vsd)["Cluster_115",]``````{r}#| fig-width: 10#| fig-height: 12# heatmap for all ASV (not only DAA)nbclusters <-2# main title mytitle <-paste("Heatmap dist(1-pearson) + ward.D2 ", "Eubiose", " n=", nrow(eubiose_vsd), " ASV" ,sep="")#color cellscellcolor_funct = circlize::colorRamp2(seq(-4, 4, length =3), c("blue", "#EEEEEE", "red"))# faster hclustht_opt$fast_hclust =TRUEht_opt$message =FALSE# annotation#GROUP_shape <- list(values = c(1, 15, 16, 17))column_annot =HeatmapAnnotation(DAY = eubiose_vsd$DAY,GROUP = eubiose_vsd$GROUP,col =list(DAY =c("D-6"="#6a3d9a", "D28"="#fdbf6f", "D51"="#e31a1c")) )# paste(unique(rowData(vsd)$Phylum), "=", brewer.pal(length(unique(rowData(vsd)$Phylum)), "Paired"))row_ha =HeatmapAnnotation(phylum =rowData(eubiose_vsd)$Phylum, col =list(phylum =c("Bacteroidota"="#A6CEE3", "Proteobacteria"="#1F78B4", "Firmicutes"="#B2DF8A", "Actinobacteriota"="#33A02C", "Verrucomicrobiota"="#FB9A99", "Desulfobacterota"="#E31A1C")),which ="row")ht <- ComplexHeatmap::Heatmap(assay(eubiose_vsd), name="abundance transformed", #abundance transformed vst and scaled by row#col = cellcolor_funct, clustering_distance_rows ="pearson",clustering_method_rows ="ward.D2", #clustering_distance_columns = "euclidean", clustering_distance_columns ="pearson", #seems UniFrac MDS#clustering_distance_columns = "binary", #seems JACCARD MDSclustering_method_columns ="ward.D2", row_split = nbclusters,row_dend_reorder =TRUE, show_row_names =TRUE, cluster_columns =TRUE, column_dend_reorder =TRUE, column_title = mytitle, column_names_centered =TRUE,column_names_gp =gpar(fontsize =8), # column_split = mycolsplit,top_annotation = column_annot,right_annotation = row_ha )ht <-draw(ht)```::: {.callout-important}After the differential abundance analysis, a hierarchical clustering followed by a heatmap plot [@Gu2016] were performed on DA ASV in at least one of the comparisons, with **ComplexHeatmap** {{< iconify mdi tools >}} R package. Abundances matrix was transformed using `vst` function from **DESeq2** {{< iconify mdi tools >}} R package to stabilize the variance and take into account for sequencing bias. Rows (=ASV) were centered and divided by the standard deviation. Hierarchical clustering was performed for both rows and columns in two steps: 1/ calculate the pearson distance (1 - corr) and 2/ apply a clustering method with the Ward's distance. :::# Upset plots::: {.callout-important}The lists of DA ASV could be compared. UpSet plots provide a visualization for exploring more than three intersecting sets. See the Shiny application: https://intervene.shinyapps.io/intervene/Here, a large part of DA ASV were shared between list of DA ASV.:::```{r}daa_asv_list <- daa_deseq2_eubiose |>map(\(x) dplyr::select(x, ASV) |>t() |>as.character())daa_deseq2_eubiose_upset <-make_comb_mat(daa_asv_list, mode ="distinct")daa_deseq2_eubiose_upsetUpSet(daa_deseq2_eubiose_upset)```| | Description ||------|------|| {{< downloadthis ../html/comparisons_alpha_diversity_rareAll_eubiose_withoutR.xlsx >}} | Excel file containing the results of alpha diversity tests for eubiose samples with rarefaction based on the complete study || {{< downloadthis ../html/daa_deseq2_eubiose_withoutR.xlsx >}} | Excel file containing the results of differential abundance analysis concerning eubiose contrasts |# Reproducibility token```{r}sessioninfo::session_info(pkgs ="attached")```# References